If you are concerned about low testosterone levels, you might be surprised by hearing that just fixing your zinc intake can make a big difference. In this article, we'll review the link behind zinc and testosterone to understand whether zinc can boost testosterone.
Testosterone levels tend to decrease naturally as we age. This decline affects normal body functions and overall health. Zinc is a great nutrient to help you address those health issues, especially low testosterone.
Zinc consumption is associated with a wide range of health benefits. It supports a healthy immune system, helps create and repair DNA, and is essential for cell growth and repair.
If you are interested in learning how zinc aids the body, read this article to learn more.
What is Zinc, and What Does Zinc Do for Your Body?
Zinc is an essential mineral for many of the body's normal functions. It supports healthy immune function, DNA synthesis, hormone production, and wound healing.


Zinc plays an important role in the production and action of testosterone. Although the formulation of zinc with magnesium has been shown to increase levels of testosterone by 30%,(1) zinc seems to be the most effective in people who suffer from zinc deficiency.(2) Also, zinc deficiency often goes hand in hand with testosterone deficiency.
Since the body doesn't make zinc, it's important to get enough of it through food or supplements.
People with inadequate zinc levels may likely experience hair loss, frequent infections, diarrhea, skin problems, and a loss of appetite.
Pros
- Helps the body fight colds and infections
- Skin protection and wound healing
- Suports healthy testosterone levels
Cons
- Supplements can cause nausea.
- Excessive amounts may hinder the absorption of other minerals.
What Are the Health Benefits of Zinc?
Many clinical studies have shown the beneficial effects of zinc in healthy adults.
Zinc intake can bring several of the health benefits below:
- Healthy Immune System: zinc supplements improve your body's ability to fight infections such as the common cold.(3) People who have low zinc levels have weak immune function and are more susceptible to respiratory infections.


- Reduce Inflammation: due to its regulatory role in the immune system, zinc has inflammatory properties.(4) It helps reduce oxidative stress, which can benefit conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes.
- Aids in Fertility Problems: Zinc appears to aid fertility(5) in both males and females. Low amounts of zinc can decrease sperm quality and testosterone levels.
Zinc and Testosterone: Does Zinc Boost Testosterone?
Zinc and testosterone production are closely related. It is a well-established fact that severe and moderate zinc deficiency in men is associated with hypogonadism (abnormally low testosterone levels).(2)
Testosterone is a vital male sex hormone. It regulates sex drive, helps bone and muscle development, and regulates optimal testosterone levels in men.


Zinc is an essential mineral for male fertility, healthy testosterone maintenance, and the overall health of the male reproductive system.
Zinc can lower the amount of sex hormone-binding globulin in the body. This can help raise free testosterone levels by stopping SHBG from binding to testosterone.
Are There Any Side Effects to Having Too Much Zinc?
Having too much zinc with food, even over 100 mg/day, does not seem to pose any health risks. However, taking too many zinc supplements may result in adverse effects, such as:
- Nausea and Vomiting: taking zinc supplements, especially in high doses, is likely to cause nausea and vomiting.(6)


(NOTE: If you suffer from zinc toxicity, seek professional medical advice immediately.)
- Changes in taste: sufficient zinc intake supports normal and healthy taste perception. On the other hand, taking too much zinc can result in hypogeusia, a dysfunction of your ability to taste. It appears as a metallic or objectionable taste in the mouth.(7)
Other than that, mild symptoms of zinc toxicity include:
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- Loss of appetite
- Headaches
What Are the Signs of Low Zinc Levels?
Several symptoms are likely to appear if you do not have enough zinc in your body.
These symptoms can range from frequent colds to blood sugar issues, or even muscle loss and infertility due to low testosterone.
The most common and obvious symptoms of zinc deficiency are:
- Frequent infections: people who are zinc deficient are more likely to have frequent colds and other infectious disorders.(8) This is due to the key role of zinc in regulating the immune function.
- Hair loss: due to the role of zinc in hair growth, zinc deficiency commonly manifests with hair thinning and hair loss.(9)


- Acne Breakout: zinc deficiency is associated with acne breakouts and severity. Taking zinc may help clear breakouts due to its anti-inflammatory properties.(10)


- Delayed wound healing: zinc deficiency causes cuts and scrapes to heal longer because your body relies on zinc to repair cells and tissues.(11)

- Low Testosterone Levels: Low test levels are also one of the symptoms of zinc deficiency. Low T-levels are detrimental to men's health as they are likely to experience low sex drive, weight gain, depression, and muscle loss. Zinc deficiency also contributes to male infertility due to decreased sperm count and low sperm quality.(12)


Other common symptoms of zinc deficiency include diarrhea, emotional lability, mental issues, and impaired taste and smell.(13)
If you have zinc deficiency, the best course of action is to fix your diet and take additional zinc supplements, if needed.
How Much Zinc Do You Need?
The endocrine system is made up of hormone-secreting glands. These hormones control most body functions, such as growth, metabolism, sleep, and reproduction.
To keep your endocrine system functioning correctly, you should consume at least 15 mg of zinc daily.


This dosage is enough for most people to prevent zinc deficiency and support body processes that require zinc.
However, you should not consume more than 40 mg of zinc daily from supplements for more than a month. As mentioned earlier, excessive zinc intake can lead to toxicity. However, you should be fine getting more than that from food.
Some medical conditions can deplete body stores of zinc, which may require you to take zinc supplements. Make sure you consult with your medical doctor before doing so.
What Are the Best Ways to Increase Zinc Levels?
There are a few main ways to increase zinc levels. All you need to do is consume a variety of zinc-rich foods, mostly animal products, and find a good zinc supplement to get you covered.
If you are wondering how it works, read the section below.
Zinc Supplementation
The way to optimal testosterone should ideally start with restoring normal zinc levels. Zinc supplementation is probably the most popular way to achieve adequate zinc levels in the body. There are several forms of zinc supplements, and all of them can be bought on major retail websites and at local pharmacies.


Here are some of the best products that increase both testosterone and zinc levels.
- TestoPrime
- Testogen
- Prime Male
- Testodren
- TestoFuel
- Testo-Max
- TestRX
However, before taking any supplements, make sure you get advice from your healthcare provider to avoid negative side effects.
Zinc Food Sources
If investing in zinc supplements is not for you, zinc-rich food is always the best bet.
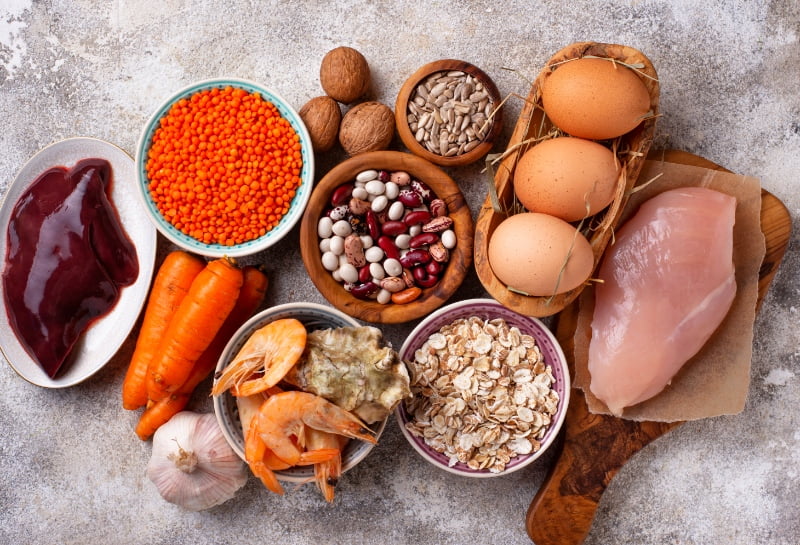


Foods high in zinc include:
- Meat
- Shellfish
- Nuts
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Whole grains
Zinc and Other Hormones
Zinc has different functions and effects on the other hormones in the body, which allow them to perform their normal physiological functions.


Some of the hormones influenced by zinc include:
- Growth Hormone: Growth hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland. It is responsible for growth and development of all body cells. The growth hormone regulates muscle growth, bone growth rate, and fat metabolism. Zinc deficiency can negatively impact growth by negatively affecting the levels of growth hormone and its metabolites.(14)
- Thyroid Hormones: Zinc is needed for the synthesis and action of thyroid hormones in the body.(15) Low zinc levels can lead to hypothyroidism.
- Luteinizing Hormone: LH is the hormone responsible for stimulating testosterone production. If you are producing too much testosterone, the hypothalamus will alert the pituitary gland(16) to reduce the production of LH, which can lead to a decreased secretion of testosterone. If you have a zinc deficiency, it can lead to impaired synthesis or secretion of LH and decreased testosterone production.
FAQ:
We know that low testosterone levels leave men worried and raise many questions. Here are some of those questions answered.
Must I Have Low Test to Be Deficient in Zinc?
It is possible to have low testosterone levels without having a zinc deficiency, and vice versa. This is because other factors like aging, chronic illness, or even an unhealthy diet and lifestyle can cause your testosterone levels to go down.
How Long Does It Take for Zinc Products to Increase Testosterone and Show Results?
A recent study(17) found that zinc increases testosterone after 20 weeks of consistent supplementation. If you want to rapidly increase your zinc status and serum testosterone levels, you should pair your zinc intake with regular exercise, healthy diet, and other natural dietary supplements with testosterone-boosting ingredients.
How Does Zinc Affect Male Sexual Health and Libido?
Zinc helps increase testosterone levels, especially in men who suffer from zinc deficiency. Thus, zinc also assists in improving male arousal and erection maintenance. On the other hand, a lack of zinc can also contribute to sexual dysfunction, low libido, and infertility.
Why Is Zinc Essential for Health and Exercise?
Zinc is essential for your health and exercise, as it supports your body's metabolism, digestion, nerve function, and many other functions. Zinc also maintains healthy skin and helps produce proteins and synthesize DNA.
What if I Have Low Testosterone but Am Not Deficient in Zinc?
Low testosterone can be caused by a number of different factors, not just zinc deficiency. These may include aging, a poor diet, and a lack of sleep and exercise. Finding the cause and the best way to address it should only be done with your healthcare practitioner.
How Do Athletes Benefit From Having Enough Zinc?
Athletes, in particular, have an increased need for zinc to maintain their muscular physique and athletic performance. Proper zinc intake can boost the immune system and aid in muscle repair. Zinc deficiency often puts athletes at risk for delayed recovery and various health issues, like frequent infections or muscle weakness.
Conclusion: Does Zinc Really Boost Testosterone Levels?
If you suffer from low testosterone symptoms, zinc is one of the best minerals to support optimal testosterone production.


Zinc also helps fight colds and infections, maintains skin health, speeds wound healing, and can even help treat erectile dysfunction, increase sex drive, and improve muscle mass.
Make sure you estimate your dietary zinc intake before starting with zinc supplements.
- Brilla, Lorraine R and Victor Conte. “Effects of a Novel Zinc-Magnesium Formulation on Hormones and Strength.” (2000).↩
- Prasad, A S et al. “Zinc status and serum testosterone levels of healthy adults.” Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.) vol. 12,5 (1996): 344-8. doi:10.1016/s0899-9007(96)80058-x↩↩
- Shankar, A H, and A S Prasad. “Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection.” The American journal of clinical nutrition vol. 68,2 Suppl (1998): 447S-463S. doi:10.1093/an/68.2.447S↩
- Prasad, Ananda S. “Zinc: an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent: role of zinc in degenerative disorders of aging.” Journal of trace elements in medicine and biology: organ of the Society for Minerals and Trace Elements (GMS) vol. 28,4 (2014): 364-71. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.07.019↩
- Fallah, Ali, et al. “Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men's Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization.” Journal of reproduction & infertility vol. 19,2 (2018): 69-81.↩
- Fosmire, G J. “Zinc toxicity.” The American journal of clinical nutrition vol. 51,2 (1990): 225-7. doi:10.1093/ajcn/51.2.225↩
- Bilici, Mustafa et al. “Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of zinc sulfate in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.” Progress in neuro-psychopharmacology & biological psychiatryvol. 28,1 (2004): 181-90. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2003.09.034↩
- Weiss, G, and P L Carver. “Role of divalent metals in infectious disease susceptibility and outcome.” Clinical microbiology and infection : the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases vol. 24,1 (2018): 16-23. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2017.01.018↩
- Karashima, Tadashi et al. “Oral zinc therapy for zinc deficiency-related telogen effluvium.” Dermatologic therapy vol. 25,2 (2012): 210-3. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2012.01443.x↩
- Yee, Brittany E et al. “Serum zinc levels and efficacy of zinc treatment in acne vulgaris: A systematic review and meta-analysis.” Dermatologic therapy vol. 33,6 (2020): e14252. doi:10.1111/dth.14252↩
- Lin, Pei-Hui et al. “Zinc in Wound Healing Modulation.” Nutrients vol. 10,1 16. 24 Dec. 2017, doi:10.3390/nu10010016↩
- Fallah, Ali et al. “Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men's Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization.” Journal of reproduction & infertility vol. 19,2 (2018): 69-81.↩
- Maxfield L, Shukla S, Crane JS. Zinc Deficiency. [Updated 2022 Nov 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493231/↩
- Richards, G. E., and R. N. Marshall. ‘Relationship between Zinc and Growth Hormone (GH) in GH Deficient Children’. Pediatric Research, vol. 15, no. 12, Dec. 1981, pp. 1551–1551, https://doi.org10.1203/00006450-198112000-00094.↩
- Severo, Juliana Soares et al. “The Role of Zinc in Thyroid Hormones Metabolism.” International journal for vitamin and nutrition research. Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitamin- und Ernahrungsforschung. Journal international de vitaminologie et de nutritionvol. 89,1-2 (2019): 80-88. doi:10.1024/0300-9831/a000262↩
- Root, A W et al. “Effects of zinc deficiency upon pituitary function in sexually mature and immature male rats.” The Journal of nutrition vol. 109,6 (1979): 958-64. doi:10.1093/jn/109.6.958↩
- Mazaheri Nia, Leila et al. “Effect of Zinc on Testosterone Levels and Sexual Function of Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” Journal of sex & marital therapy vol. 47,8 (2021): 804-813. doi:10.1080/0092623X.2021.1957732↩
