Testosterone is the primary male hormone that influences muscle development, body composition, and metabolic rate. This article provides a detailed overview of how testosterone changes with age and sex and what implications it has on overall health.
Testosterone is commonly associated with being the main sex hormone in men. While this is true, testosterone also plays an important role in women. Due to the obvious biological differences between males and females, testosterone is responsible for different things depending on the sex of the individual.
Testosterone levels change depending on age and sex, and this article is focused on explaining normal and average levels at different ages and detailing the health effects of low testosterone.
In men, testosterone is responsible for muscle growth and the development of male sex characteristics, including body and facial hair, testes, and the penis. Testosterone also influences sperm production. Healthy testosterone levels are crucial for maintaining lean body mass.
For women, testosterone plays a vital role in the growth of reproductive tissue and bone mass. However, it is produced in far smaller quantities in women than in men.
Over the course of an individual's life, their natural testosterone levels can fluctuate. Numerous different factors can influence endogenous testosterone production, including diet, lifestyle, sleep habits, stress levels, medications, and supplements. Low testosterone levels can lead to serious health problems in both women and men.
If you are in doubt about your testosterone levels, it is recommended that you seek medical advice from healthcare professionals.
In this article, we’ll be discussing normal and average testosterone levels by the age of the individual. We’ll also go over the implications of low testosterone levels in both men and women.
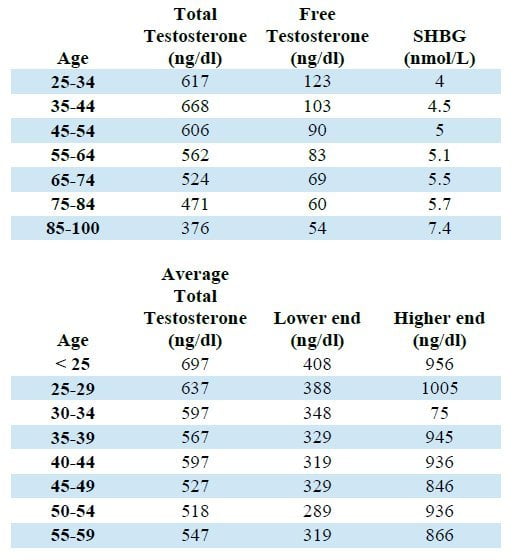
Normal Testosterone Levels By Age
Testosterone levels are measured by nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). Normal levels of testosterone change over the individual's lifetime.
Factors such as diet, lifestyle, stress levels, and sleep habits all influence testosterone levels. Chronic illness can also negatively impact During puberty, the normal range of a male’s testosterone levels could be anywhere between 300 and 1,200 ng/dL.
As men get older, their testosterone levels start to decline. Normally, this decline starts when men turn 30 years old.
If an individual starts to experience some symptoms associated with low testosterone levels, there may be another underlying cause that has nothing to do with their testosterone.
This is because the symptoms of decreased T levels are also the symptoms of a myriad of other health issues.
The only way to determine whether your symptoms are caused by low T levels is to have a blood test. However, some men and women who have low testosterone might not experience any symptoms. In this case, they could benefit from regularly checking their testosterone levels.
Average Testosterone Levels By Age
Many studies have been conducted in order to establish what average testosterone looks like across a range of age groups. Most of these studies, however, do not factor in most existing conditions or lifestyles.
This can lead to misleading data.
This being said a decline in testosterone with age is a widely accepted fact. The severity of this decline is still debated.
You might be wondering why testosterone levels decrease with age. This can be explained by looking at menopause in women. Menopause is typically a woman’s body adjusting to post-childbearing age. This decrease in testosterone levels in men is referred to as andropause.
One study conducted by Harvard Health Publishing in 2008 found that while there is a great deal of swing in the range of testosterone levels recorded in the sample, there is a steady decline in men over 40.
The testosterone measurements in that sample were as follows:
Men in their 40s: 252–916 ng/dL
Men in their 50s: 215–878 ng/dL
Men in their 60s: 196–859 ng/dL
Men in their 70s: 156–819 ng/dL
As this study shows, men in their 60s and 70s can have a testosterone level anywhere between 156 and 859 ng/dL. This is a considerable difference.
ALSO READ: Testosterone Dependence: How Real Is The Risk?
Causes of Low Testosterone
While the gradual decline of testosterone levels is almost an inevitable part of aging, people also get low testosterone for a number of reasons. These include certain health conditions, medications, and injuries, as well as dietary and lifestyle habits.
The following can negatively impact normal testosterone levels:
- Chronic illnesses, like cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome
- Secondary hypogonadism due to issues with the hypothalamus or pituitary gland
- Poor thyroid function
- Certain diseases of the testicles are caused by trauma, infection, or inflammation.
- Benign tumor of the pituitary gland that produces excess prolactin
- Chronic stress
- Obesity
- Sleep issues
The Implications of Low Testosterone
As mentioned earlier, there are serious health risks associated with low testosterone levels in both men and women. In clinical terms, low levels of testosterone are a condition known as hypogonadism. Older men usually suffer from late-onset hypogonadism, also known as testosterone deficiency syndrome. Late-onset hypogonadism is a clinical diagnosis characterized by low measured testosterone levels and mostly sexual symptoms, especially low sex drive and erectile dysfunction. Men are often offered testosterone replacement therapy as the best option to deal with low test.
The benchmark for low testosterone levels is different for men and women. Typically, low testosterone levels in men are identified at 300 ng/dL or less. In women, this number is less than 15 ng/dL or 25 ng/dL (depending on the lab) if you’re under 50 years of age, and 20 ng/dL if you're 50 or older.
Men and women with testosterone levels of 300 ng/dL or 15-25 ng/dL are said to have low levels. The clinical threshold for hypogonadism is any reading below 200 ng/dL. This is a strong indication for testosterone therapy.
A blood test to determine your testosterone levels can help explain how you feel. People who are experiencing a testosterone level of 200 ng/dL generally feel numerous symptoms of decreased endogenous testosterone production and are often recommended to start testosterone replacement therapy.
Low testosterone can manifest in men and women with a variety of symptoms.
Men with low testosterone usually experience sexual symptoms and other general health issues.
- Reduced sex drive
- Lower sperm count
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased muscle mass, decreased lean body mass, and increased body fat
- Hair loss
- Blood pressure issues
- Metabolic syndrome
- Depression and anxiety
- Fatigue and insomnia
- Bone mass loss and poor bone metabolism
- Cognitive issues
Low testosterone in women usually presents with the following symptoms:
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Osteoporosis/loss of bone density
- Weight gain
- Menstrual irregularities/fertility problems
- Depressive symptoms
- Decreased sex drive and sexual dysfunction
- Decreased lean body mass
ALSO READ: Best Testosterone Booster for Women
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Let's look into the most common age-related testosterone questions.
Why Do Testosterone Levels Vary By Age?
Testosterone levels naturally vary with age due to biological processes, including hormonal changes and gradual decline in testosterone production as you grow older.
Can Low Testosterone Levels In Older Adults Be Treated?
Yes, treatment options include testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). Consult a healthcare provider to discuss potential benefits and risks before starting any treatment.
Conclusion
Although the gradual decline of testosterone levels is associated with normal aging, you don't have to suffer from the negative effects of lower T levels. If you or someone you know has any of the symptoms mentioned above, it may be a good idea to check their testosterone levels.
There are a range of treatments available for people with low T levels. The most common one is known as testosterone replacement therapy.
This therapy doesn’t stimulate the body to increase endogenous testosterone production. Instead, it provides exogenous testosterone to help quickly increase and maintain normal hormonal levels. TRT works best when prescribed by experienced doctors who make sure the appropriate dosage is prescribed.
Women with low testosterone should receive a variety of treatments as there might be an underlying health condition influencing T levels, such as polycystic ovary syndrome.
The use of certain medications, dietary supplements, or lifestyle changes is common to help manage lower T levels in both men and women. Always work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan tailored to you.